You’re setting goals. Publishing content. Reporting on growth.
But deep down, you’re still asking: “Are we aiming too high? Too low? Are we even on track?”
That uncertainty is normal — but it’s also a signal that you need an SEO forecast.
At Backlinko, we do SEO forecasting throughout the year. We use it to map planned content, track production costs, and project traffic and revenue gains.
This approach lets us prioritize effectively. Pivot when content underperforms. And build lasting trust with our stakeholders.
As Leigh McKenzie, our Head of SEO puts it:
“Forecasting is hard, and imperfect, but it’s essential. It forces you to tie effort to outcome. And to build trust, we always present a range (best case, expected case, and failure case), not just a single optimistic projection. That honesty helps us make better decisions — and earn buy-in.”
This guide gives you two proven forecasting methods.
Plus, a spreadsheet to project SEO traffic in minutes, right now.
Just upload your site’s performance data from Google Search Console (GSC), and this SEO forecasting tool will do the calculation for you:
If you’re the kind of person who learns best by doing, you don’t have to wait. Jump right in with our forecasting template.
Download the FREE SEO Forecasting tool now.
Follow along step by step as we break down each method, or just punch in your GSC data and start forecasting right away.
Quick Overview of SEO Forecasting Methods
There are two ways to predict your SEO growth:
- Keyword-based forecasting: great for modeling new topics or page opportunities
- Statistical trend analysis: ideal for projecting growth based on your past SEO performance
But, which one should you choose?
Here’s a brief overview:
| Scenario | Keyword-Based Forecasting | Statistical Trend Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Your website has steady traffic (24+ months of data) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Your website is fairly new (limited data) | ✓ | ✗ |
| You want to target new/trending keywords | ✓ | ✗ |
| Your business is seasonal | ✓ | ✓ |
Let’s go through both approaches step by step, starting with the simplest option:
Approach #1: Keyword-Based Forecasting
Forecasting SEO traffic based on keywords means predicting how much organic traffic you could earn from specific search terms.
You can make an SEO forecast based on keyword data manually or with an SEO keyword tool.
Calculate Forecasted Traffic Manually
You can calculate your potential traffic with this simple formula:

Let’s break this down with an example.
Imagine you’re creating a page targeting the keyword “best hiking boots for women.”
The keyword has a search volume of 10,000 monthly searches
Your current content ranks around position 10, but you’re aiming to improve it to position six after optimizations.
Based on your historical data, you know that pages ranking at position six typically get about 2% CTR.
Using the formula:
10,000 × 2% = 200 estimated monthly visits for that keyword
While this is a simple formula, it comes with limitations.
It doesn’t account for seasonal variations, competition changes, or CTR shifts over time.
If you want to make more sophisticated keyword-based predictions, use tools like Semrush.
Its algorithms are built to provide more nuanced forecasts that account for various factors influencing SEO performance.
Here’s how:
Estimate Keyword-Based Traffic with Semrush
Open Semrush’s Keyword Overview tool. Enter your target keyword and your domain, and click “Search.”
Let’s say you’re planning to target a new topic cluster, “memory foam mattress” on a mattress brand website, Casper:
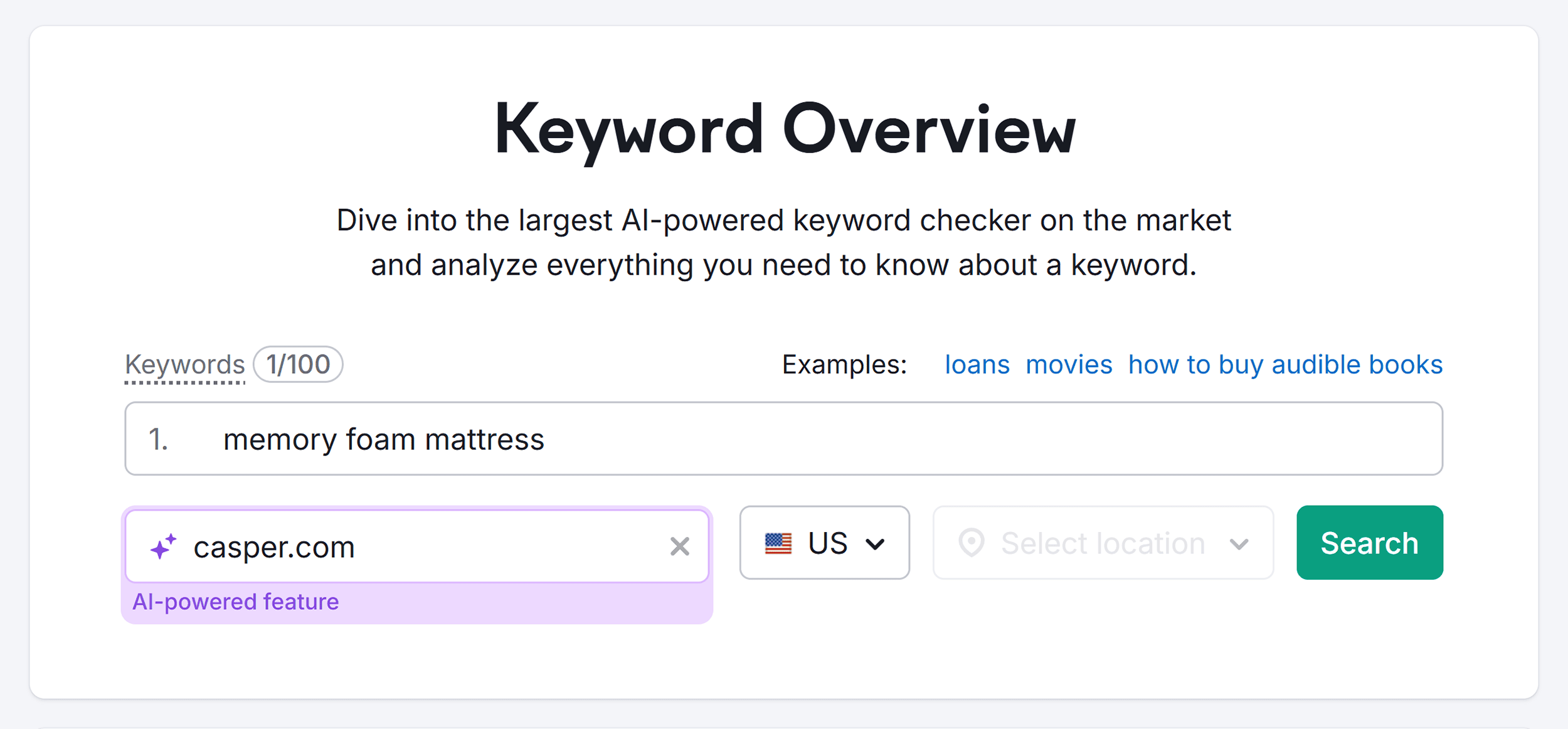
After analyzing the keyword and your website, the tool will provide predictions in three areas:
- Potential traffic: Estimated monthly visits you could earn from a specific keyword, based on your website authority and expected ranking
- Potential topic traffic: Total monthly traffic potential from all keyword variations related to the topic
- Potential position: Where your page is likely to rank in the search engine results page (SERPs), compared to competitors in the top 10

So, Semrush predicts that you’ll potentially get 1,000 visitors per month if you target the keyword “memory foam mattress.”
But there’s 2.6 times more traffic opportunity if you write high-quality content and cover the topic in more depth.
To identify related keyword opportunities, click “See topic details.” It’ll give you a broader list of related search terms:

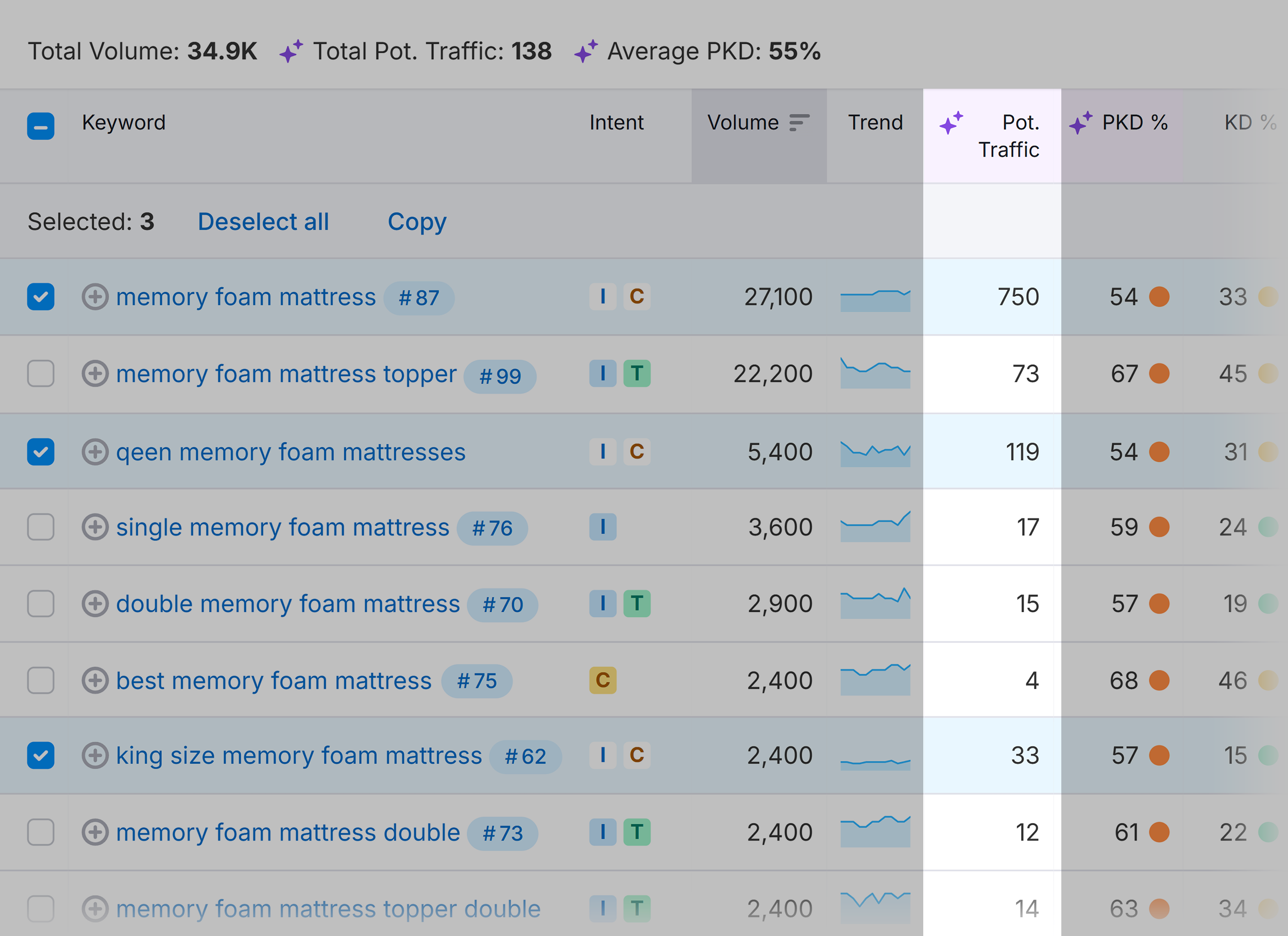
When analyzing these keywords, pay attention to the following metrics:
- Trend: Is the search volume growing or declining over time
- Potential traffic: Estimated visitors for each keyword based on your site’s authority
- Personal keyword difficulty (PKD%): How challenging it would be for your specific domain to rank in the top 10
Note: A free Semrush account gives you 10 searches in this tool per day. Or, you can use this link to access a 14-day trial on a Semrush Pro subscription.
Interesting read: Choose Keywords: A 6-Step Essential Guide
Approach #2: Statistical Trend Analysis
If your site has at least 16-24 months of traffic data, statistical trend analysis is the most reliable way to forecast growth.
Why?
Statistical trend analysis relies on your actual traffic data. Not guesswork, not keyword volume projections, but how your site has performed over time.
It’s also the most technical method.
Normally, this kind of forecasting would require time series modeling or scraping in Python.
But to make it more accessible, we’ve built a custom SEO forecasting spreadsheet that handles the math for you.
Get your FREE SEO Forecasting Spreadsheet here
We created this template in partnership with Andrew Charlton from Crawl Consultancy to help you run statistical forecasts in just a few clicks.
You don’t need any coding or advanced modeling skills (I’ll guide you exactly how to use it in a bit).
All you need is to import your site’s past performance data. The spreadsheet will show your forecast summary, growth scenarios, and monthly breakdown.
Here’s a preview of the dashboard you’ll be working with:

Simple, right?
Here’s how to use this SEO forecasting tool, step by step:
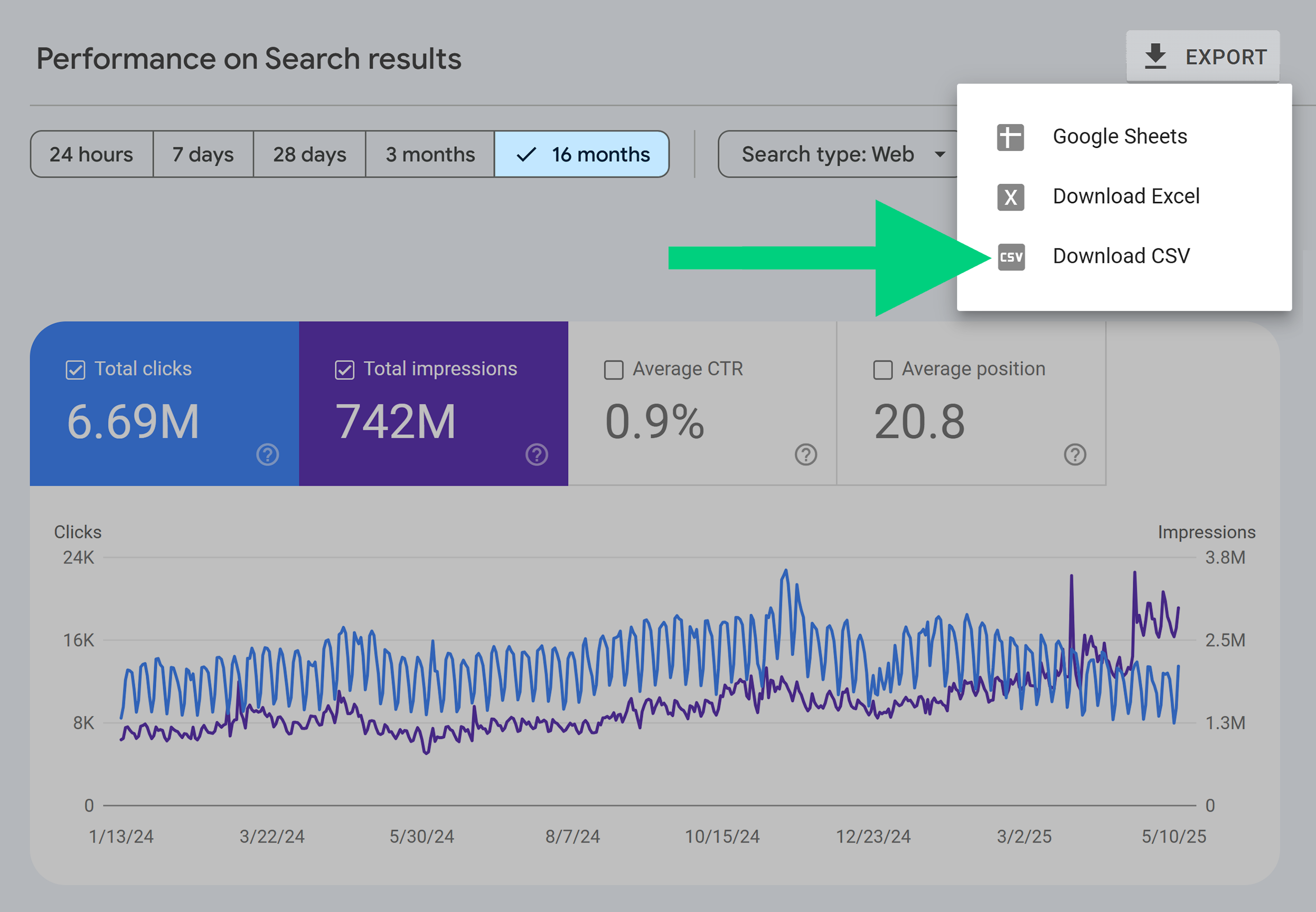
Step 1: Export Your Google Search Console Data
First, get your raw data from GSC. You’ll need the last 16 months of site performance to feed into the model.
Why 16 months of data?
That’s the most historical data available in Google Search Console. It’s enough to see seasonal trends and growth patterns.
To get the data from GSC:
- Open Google Search Console
- Select your property and go to the “Performance” tab
- Set the date range to cover the last 16 months
- Click “Export” and choose “Download CSV”
- Unzip the file — you’ll see one named Dates.csv
Step 2: Import the CSV File Into the Spreadsheet
Now, plug that GSC data into the spreadsheet:
- Go to the [2] Google Search Console Import tab
- Click on the marked cell (usually the top-left of the table)
- In Google Sheets, navigate to “File” > “Import” and upload your Dates.csv file
- Under “Import location,” choose “Replace data at selected cell” and click “Import data”

The sheet will clean and structure your click data, group it by month, and feed it into the forecasting model.
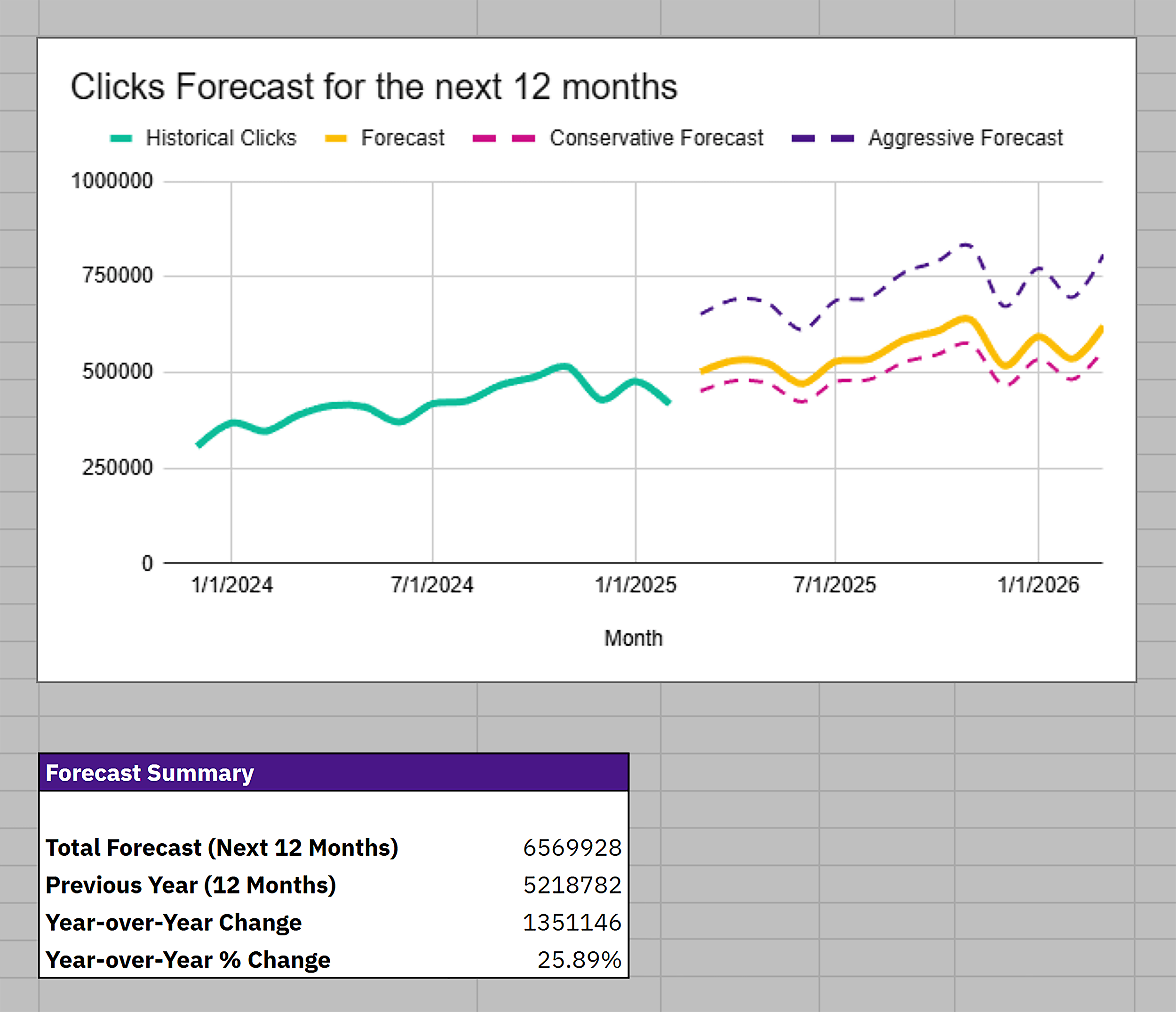
Step 3: Review Your 12-Month Forecast
Once the data’s in, head to the “Dashboard” tab.
Here, you’ll see:
- Your total forecast for the next 12 months
- A comparison against your previous 12 months
- The year-over-year (YOY) change in clicks and %
- A line chart visualizing your predicted traffic over time
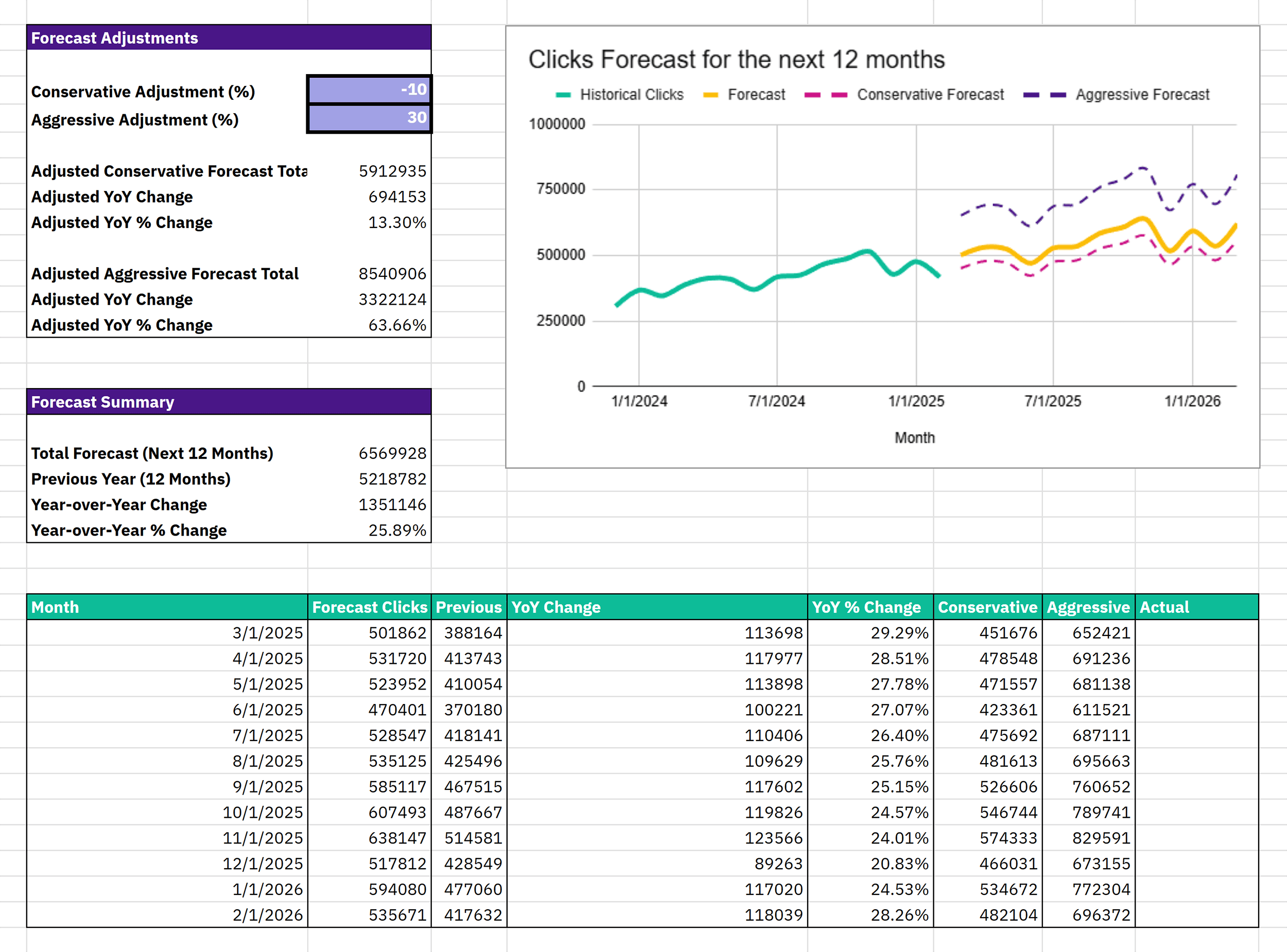
Note: This forecasting is based on a simple linear regression, making it easy to explain the forecast. Even to non-SEO folks.
Step 4: Adjust Growth Scenarios
SEO traffic rarely grows in a straight line. That’s why forecasting different scenarios helps you stay realistic and better prepared.
In the “Forecast Adjustments” box, you’ll find two fields:
- Conservative Adjustment (%): E.g., -10% for a cautious projection
- Aggressive Adjustment (%): E.g., +30% for a stretch goal
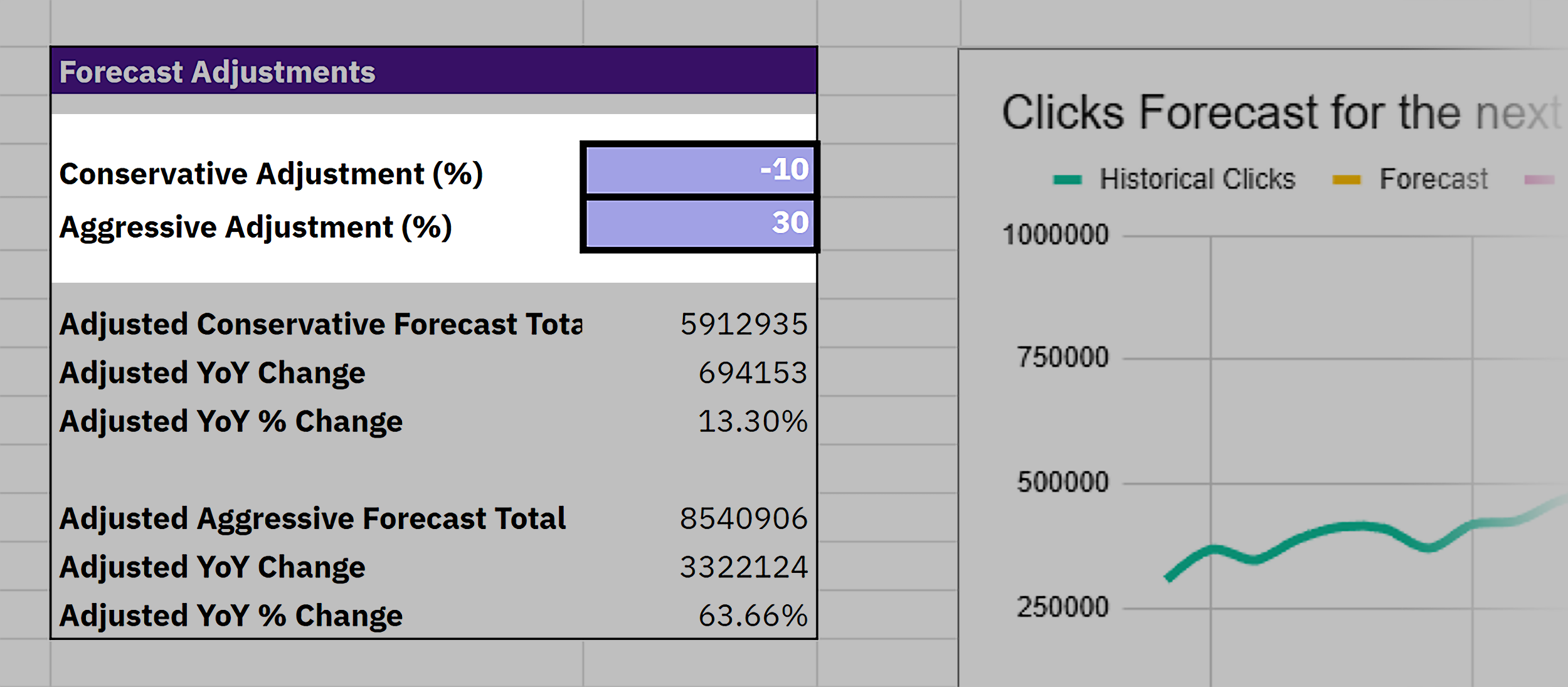
Once you enter values, everything updates automatically — scenario totals, YOY change, graph lines.
Note: This lets you test “what if” outcomes, which is perfect for stakeholder reporting or planning quarterly targets.
But, why do we do this?
Let’s say your site has been growing at ~5% per month. However, next quarter, you’re planning to:
- Publish 10 new optimized blog posts
- Refresh your top-performing evergreen content
- Run a PR campaign that usually brings high-authority backlinks
Useful resource: How to Write a Press Release That Gets Results (2025)
Based on similar past campaigns, you estimate this could boost your organic traffic by 20-30%.
So, you enter +30% in the Aggressive Adjustment field.
Now imagine the opposite:
Budget cuts slow down content production, or your writer’s on leave.
You’d weigh that in and enter, let’s say, -15% in the Conservative Adjustment to reflect that slowdown.
If you’re not sure what numbers to put in these fields, here are some places to start:
- Past internal data: Look at traffic lift from similar initiatives (e.g., “last time we launched 10 blog posts, traffic increased by 18% in two months”)
- Operational inputs: Fewer resources, delayed launches, or technical issues? Model that in with a -10% to -20% dip.
- External benchmarks: Use data from tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or industry studies to inform your assumptions (e.g., “content updates to your competitors’ sites led to +15% traffic on average”)
Even if your percentages aren’t perfect, the act of modeling a range makes your forecast stronger and way more reliable.
How to Present Your SEO Forecast
A clear presentation turns your traffic projections into a strategic tool. One that you can use to align your team, make a case for investment, or guide quarterly planning.
Here’s how to present it effectively:
1. Start with a Visual Overview
Begin with a chart that shows your traffic forecast over time — whether that’s based on keyword data or historical trends.
Why lead with a visual?
Charts turn raw numbers into a clear story. They show trends, dips, and momentum at a glance. Like this:

And this helps stakeholders understand where you’re headed without having to dig into spreadsheets or data tables.
The goal is to answer this question at a glance: “What kind of growth are we expecting, and how confident are we in that number?”
If you’re using our spreadsheet template, the built-in dashboard does this for you:

You can:
- Share your screen and walk through the forecast live
- Take a screenshot of the chart and summary and paste it into a report or slide deck
- Export the chart as an image to use in a strategy doc
Pro tip: If you need something more advanced or reusable, you can recreate the chart in Google Looker Studio — a free tool for building custom reporting dashboards.
If you’re using Semrush to estimate traffic potential for new content, you can still visualize it.
Let’s say you’re targeting the “memory foam mattress” topic and want to target the following keywords:
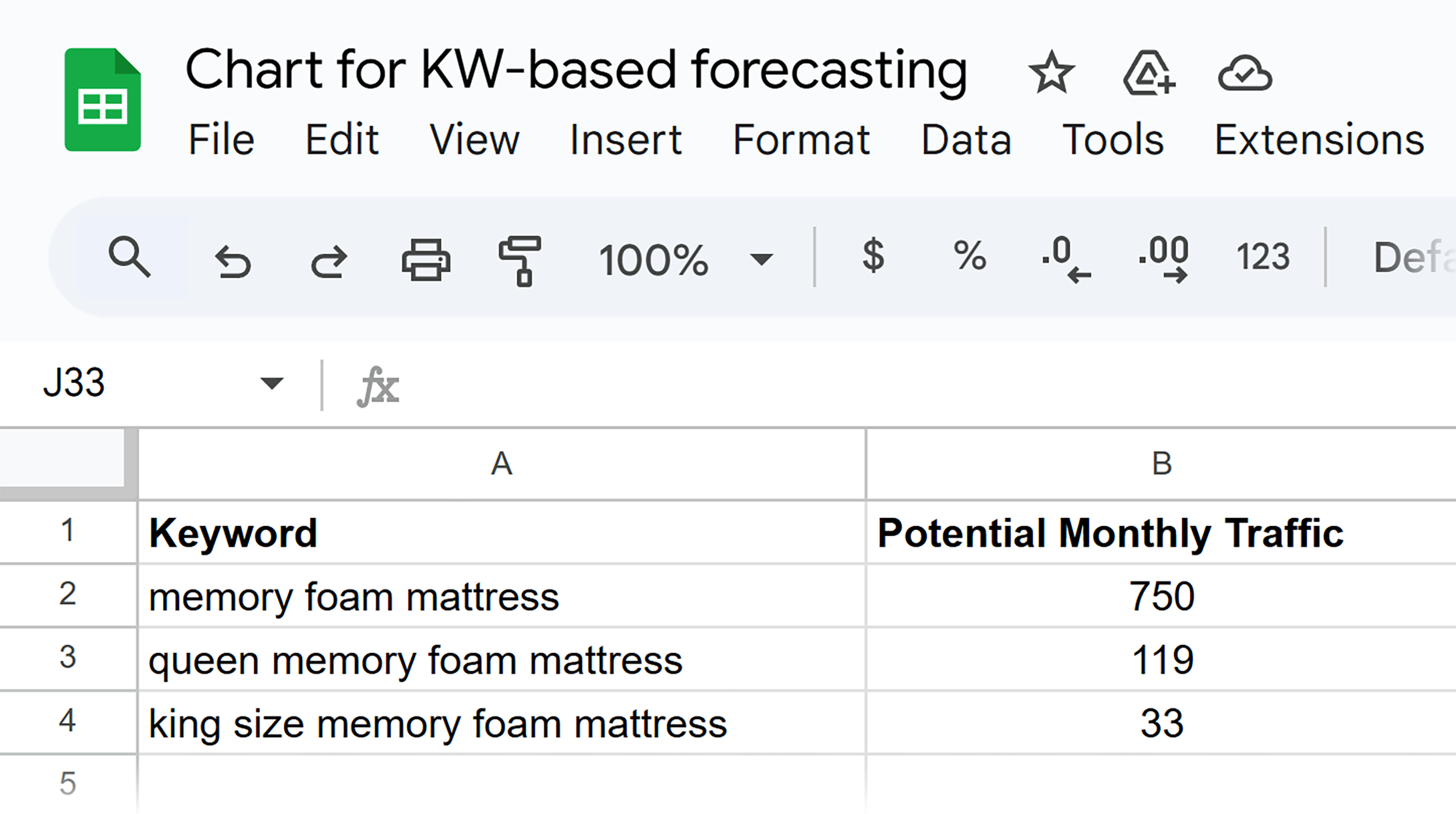
- “memory foam mattress” — 750 potential visits/month
- “queen memory foam mattress” — 119 potential visits/month
- “king size memory foam mattress” — 33 potential visits/month
Create a new Sheet and enter your keywords and potential monthly visits. A simple one, like this:
Then, insert a bar chart to show estimated traffic per topic with potential traffic on the x-axis and each keyword (or topic cluster) on the y-axis.
Like this:
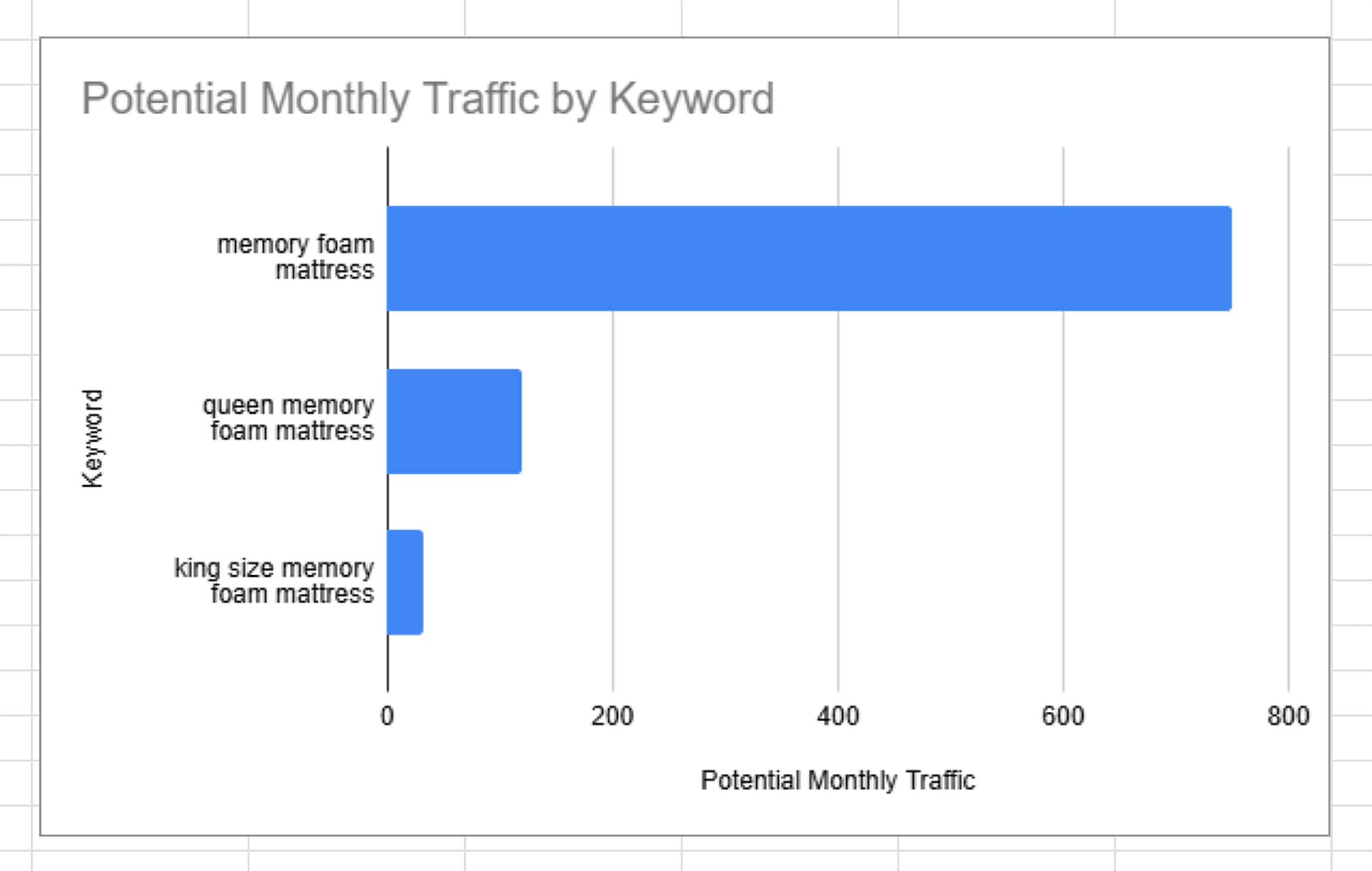
Note: This gives you and your stakeholders a quick way to see which topics are worth prioritizing. And how much they might contribute to your organic growth.
2. Frame It Around Business Outcomes
Don’t just show how traffic might grow.
Show why it matters, too.
In your presentation, lead with:
- The expected growth potential
- What content or actions will drive that growth
- How it supports high-level goals like lead generation, revenue, or product visibility
The clearer the link between SEO activity and business outcomes, the easier it is to get support and alignment.
3. Connect Your Forecast to Potential Revenue
While traffic forecasts are powerful, tying them to business results makes them even more persuasive.
If you want to show potential ROI, you can estimate how much revenue your forecasted traffic might drive using a simple formula:
Forecasted Monthly Traffic × Conversion Rate × Revenue per Conversion = Estimated Monthly Revenue
Let’s say your forecasted traffic is 10,000 visits per month. Your site’s average conversion rate is 2% and each conversion gets you $150.
Using this formula, your estimated monthly revenue would be:
10,000 × 0.02 × 150 = $30,000/month
4. Be Transparent About Your Assumptions
A good forecast is grounded in clear logic, and people are more likely to trust it when they understand how you built it.
So, share:
- Where your data came from (e.g., GSC, keyword tools)
- The method you used (trend analysis, keyword-based, or both)
- What each scenario assumes and how flexible it is
You don’t need to walk through every formula. Just show that your projections are based on real data and thoughtful decisions.
Why it matters: When your process is transparent, your forecast becomes easier to trust, easier to defend, and more valuable for making decisions.
How to Keep Your Forecast Accurate
A forecast is most valuable when it evolves with your strategy. Regular check-ins help you stay aligned, catch changes early, and refine the strategy.
Here’s how to keep your forecast accurate and useful over time:
Review Your Forecast Monthly
Check in at the end of each month to compare projected vs. actual traffic.
To do so, go to your forecast dashboard and add your actual monthly clicks (from GSC) in a separate column:
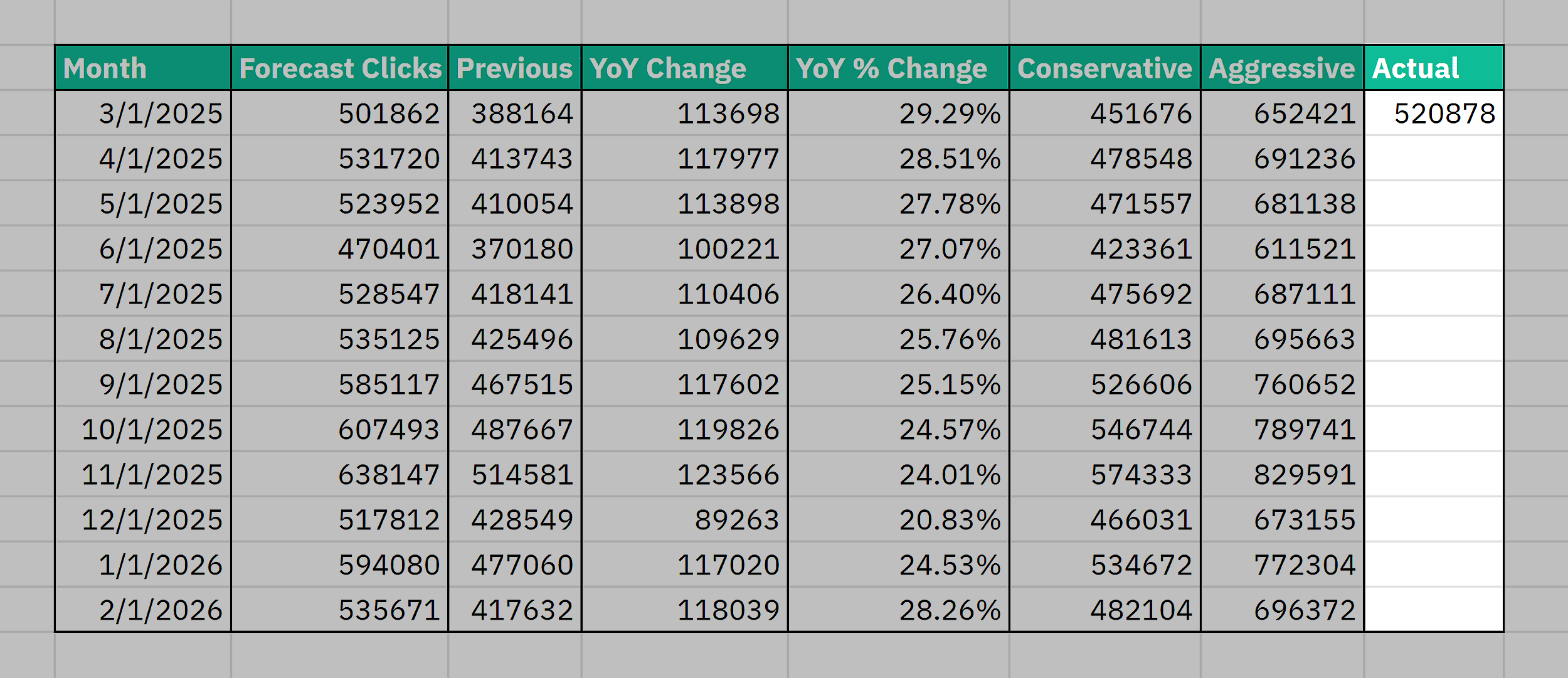
Then, compare the difference between forecasted and actual performance. Make quick notes on anything that influenced the results.
For example, a major content launch, slower publishing, or an unexpected spike.
This helps you understand whether you’re on track or not. Plus, spot the reasons why you’re ahead or behind.
Adjust Your Assumptions When Things Shift
Forecasts are based on what you expect to happen. As your content strategy evolves, your assumptions likely do, too.
How to do it:
- Revisit your growth rate or scenario modifiers in the spreadsheet (e.g., change +30% aggressive to +20%)
- If your traffic consistently trends above or below expectations, update the baseline data or adjust your model
- Rerun keyword opportunity analysis if SERPs or seasonality have shifted
Note: Think of it as recalibrating — not correcting. These adjustments keep your forecast aligned with the current situation.
Ready to Turn Your Forecast Into a Strategy?
Now that you know how much organic traffic you can realistically drive, the next step is planning how to get there.
With the right content, priorities, and execution.
Use your forecast to:
- Decide which pages you need to create, update, or expand
- Double down on topics and clusters that can move the needle
- Set clear KPIs tied to traffic growth, rankings, or business goals
And if you’re ready to build the strategy to drive your numbers, check out our guide: How to Create an Effective SEO Strategy in 2025.
The post How to Do Realistic SEO Forecasting Step-by-Step (+ Template) appeared first on Backlinko.








