Local keyword research is the process of finding the keywords people use when they’re searching for locations, products, or services in their area.
Like this:

Why are local keywords useful to know?
Keywords are a fundamental element of search engine optimization (SEO).
Search engine algorithms, like Google, consider many factors when deciding which pages to rank highly in the results for any given search. The prevalence of related keywords in your content is a major factor.
Local keyword research tells you which keywords to target in your content. Do it right, and your business becomes more visible. This means that you can attract more organic traffic to your business listings and site.
More traffic can mean more customers. And more customers means more sales.
Take Kody Smith, for example. He strategically used keyword research to inform his local SEO strategy. In doing so, he skyrocketed his former side hustle into a full-time business with nearly $300,000 in annual revenue.
Putting the effort into local keyword research gives you a chance to replicate Kody’s success.
This article provides the introduction you need to understand local keyword research. And the exact steps to perform it for your location-specific business.
Let’s dive in.
Applications of Local Keyword Research
Imagine you own a fantastic bakery and want more customers to discover your delicious treats. You’ll want to know what’s on the search engine results page (SERP) for the keyword “bakery in Joliet.”
First, you see the selection of Places. Like this:

Businesses that rank highly in Places likely have well-optimized Google Business Profiles (more on that later).
These ones probably have business descriptions that include bakery-related keywords, business categories set to “bakery,” and addresses in their listing that says “Joliet.”
That information tells Google’s algorithm that the business is highly relevant to the search term “bakery in Joliet.” So Google deems it worthy of a high rank.
Next, you’ll see the standard search results. Like this:

These websites may have earned a high SERP ranking, at least in part, by including the target keyword “bakery in Illinois” on their site. It may appear on the homepage, about us page, contact page, and blog.
Aim to earn a spot as high in the search results as possible. Ideally, among the top three results in the Places section. Or the top 10 in the standard search results. Those are the pages searchers are most likely to open.
Keyword inclusion can make a huge impact on your business’ visibility in search.
For example, Milano Bakery has 391 relevant keywords on its website. It ranks #1 for the keyword “joliet bakery.” And it gets an estimated 3,000 site visits per month from desktop searches alone.

General vs. Local Keyword Research
When you do general keyword research, you aim to understand the terms that people use to describe companies, products, or services like yours. It’s the best approach for businesses that operate nationally or globally and don’t have a local model.
Local keyword research helps you understand how people are searching for companies, products, or services like yours in a specific geographic area.
The biggest difference between general and local keyword research is keyword structure.
General keywords might be “best coffee beans” or “floss picks.” Local keywords include location-specific terms. Like the state, city, or neighborhood (e.g., “best coffee shop in Miami” or “dentist near me”).
A big part of local keyword research is identifying the exact location-specific modifiers your audience uses in their searches. Especially for businesses like yours.
Local Intent: Implicit vs. Explicit Keywords
Local intent refers to a searcher’s desire to find results relevant to their geographic location. Google is pretty good at figuring this out. It uses several signals to determine when someone is looking for local businesses or information.
One clear clue to Google is the presence of explicitly local keywords in the search. For example, “bakery in Miami” or “restaurants near the Miami Zoo.”
However, Google also considers implicit local intent. This is when a search doesn’t explicitly mention a location, but the user is looking specifically for results near them.
Google uses a variety of factors to determine local intent. Such as:
- The type of business: Phrases like “bakery” or “dry cleaners” typically indicate local search intent.
- The searcher’s location: Google can use your IP address and other signals to understand where you are.
- Search history: If you’ve been searching for local businesses recently, Google is more likely to assume you’re doing it again.
When researching keywords, you’ll definitely want to focus on those with explicit local intent. Like “bakery in Miami.”
But don’t forget about implicit local intent, either. Many people simply search for “bakeries” while they’re in your area. And you want to make sure your business shows up in those results as well.
How to Identify Local Keywords
You’re ready to find the best keywords to bring targeted customers to your business. This process has four simple steps:
- Create a spreadsheet for your keywords
- Brainstorm your seed keywords
- Find local keywords
- Use data to prioritize which keywords to target
Let’s begin.
Step 1: Create a Spreadsheet for Your Keywords
Create a simple spreadsheet to save the keywords that will come up during your local keyword research.
A spreadsheet will keep your local keywords organized. And allow you to easily analyze them to make informed decisions for your SEO strategy.
You can use our free keyword research template to get organized. It looks like this:

In your spreadsheet, identify places to track specific keyword data. Such as:
- Monthly searches: How many times the keyword being searched each month.
- Cost per click (CPC): The average amount people are paying per click for the keyword in paid ads.
- Keyword difficulty: How difficult it is to rank for the specific keyword.
- Relevance: How relevant the keyword is to your business.
- Trend: Whether the keyword’s popularity is increasing, staying the same, or decreasing.
You’ll learn how to find these metrics in step four of this section.
Step 2: Brainstorm Your Seed Keywords
Seed keywords are the short, generic phrases most relevant to your business. For example, “French bakery.”
They’re a great starting point for keyword research. You use them to unlock a larger number of more specific, related keyword phrases. Such as “Parisian pastry near me.”
Create a list of seed keywords that might be relevant to your location-based business.
Start by brainstorming all the terms or phrases customers might search when looking for businesses like yours. Irrespective of location. For example: “bakery,” “French bakery,” “fresh bread,” or “desserts.”
Then, think of location-specific terms your audience might add to their search to describe your local area. For example, “in Miami,” “near South Beach Miami,” or “near me.”
People might specify a location for their search using:
- Local landmarks: “bakery near Crandon Park”
- Street names: “bakery on Ocean Drive”
- Neighborhoods: “bakeries in Brickell”
- ZIP codes: “bakeries in 33101”
Make sure to record any generic, short phrase that represents your business.
Step 3: Find Local Keywords
In the previous step, you brainstormed the seed keywords. Phrases your customers might be using in searches for businesses like yours.
Now, you’ll use that list to discover a wider range of highly relevant and specific keywords with local search intent.
Here’s why it’s important:
- Relevance: Specific keywords with location details attract users actively looking for businesses in your area.
- Lower competition: Specific keywords are often less competitive than broad seed keywords are. This makes it easier to rank higher in search results for these terms.
- Higher conversion potential: More specific keywords indicate a user is closer to making a purchase. This leads to potentially higher conversion rates.
For local keyword research, you can use the free Google Keyword Planner. It lets you search keywords by country, territory, region, or city. Like this:

For a more in-depth keyword research experience, Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool is great for finding specific keywords. As you’ll see shortly, it provides additional keyword detail and ideas for more keywords.
Enter one of your seed keywords from step one in the Keyword Magic Tool. Select your location in the drop-down. Then click “Search.”

The tool will populate a list of keywords that contain your seed keyword. Or are variations on your seed keyword. Like this:

The more terms you insert in this tool, the wider your keyword list can get and the lower the chances of missing out on the most relevant keywords.
Note: A free Semrush account gives you 10 searches in this tool per day. Or you can use this link to access a 14-day trial on a Sermrush Pro subscription.
The Keyword Magic Tool shows you keyword data like the search volume (the average number of searches per month) and keyword difficulty (how hard it is to rank for that term).
Generally, the higher the search volume, the more people can find your business if you rank for that term. However, since many businesses use high-volume keywords, competition for them is usually high. Finding a balance between meaningful search volume and achievable keyword difficulty is key.
The data that Keyword Magic Tools shows you can help you decide which keywords to pick.
The Keyword Magic Tool also allows you to apply filters to narrow your keywords list. Let’s take a look at how you can apply filters for researching explicit and implicit keywords.
Finding Explicit Local Keywords
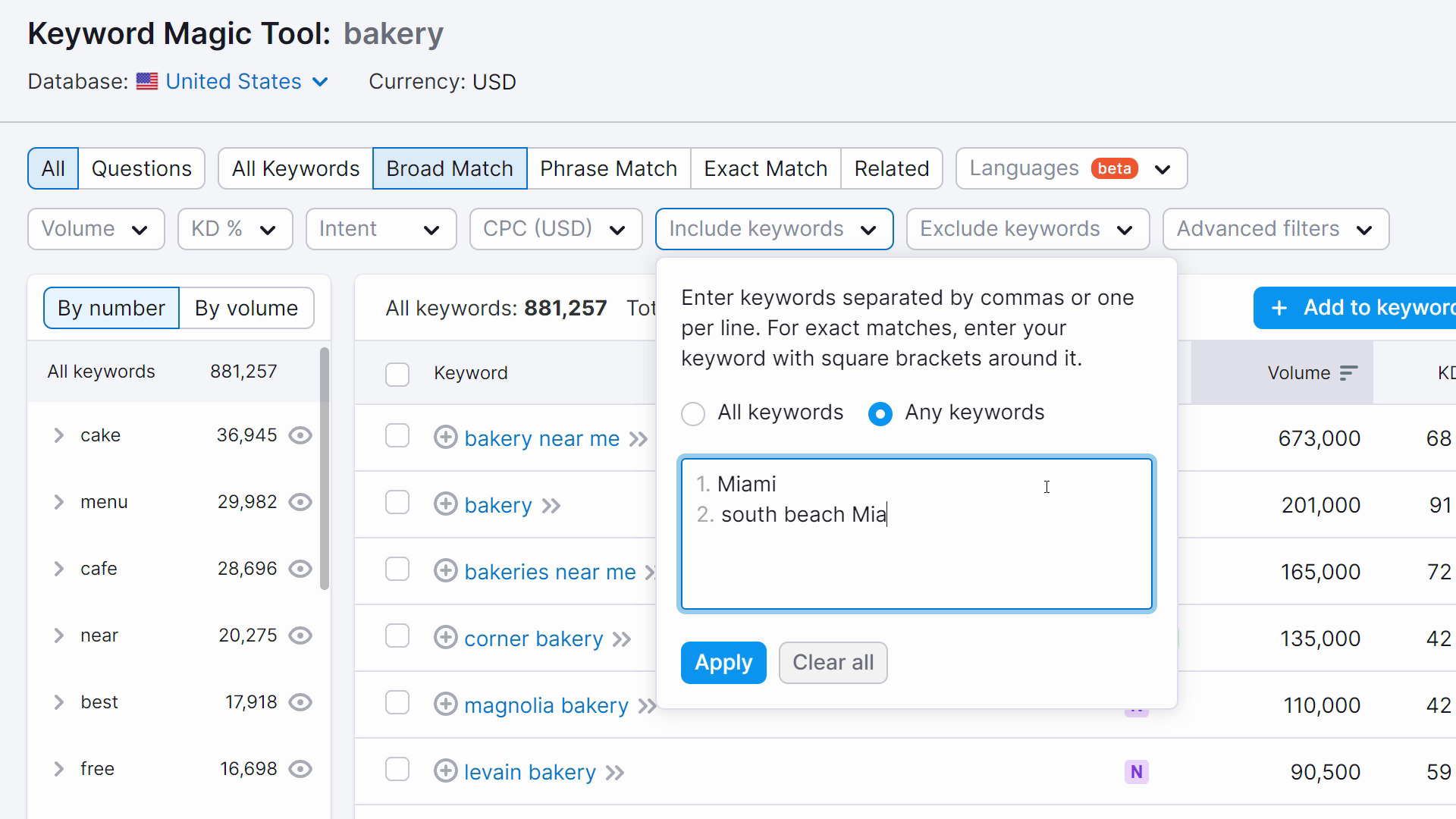
The best way to find explicit local keywords is to add your location modifiers from step one.
Click the “Include keywords” drop-down to start. Then, select the “Any keywords” option.

Type your location-specifying modifiers one at a time, pressing “Enter” or “Return” between each one.
As you find relevant keywords for your business, add them to your spreadsheet from step one. If your business is just getting started with SEO, prioritize keywords with a lower KD%, which means a score of 0-49%.
This way, you’ll be able to easily build a keyword strategy and track your results later on.
Now that you have your explicit keywords, look for implicit ones.
Finding Implicit Local Keywords
In the previous step, you added your location modifiers to filter the results. To find implicit keywords, move your location modifiers from the “Include keywords” filter to the “Exclude keywords” filter.

Then, filter keywords with local intent using advanced filters:
- Open the “Advanced filters” drop-down
- Click the “SERP Features” drop-down
- Scroll down and select “Local pack”
- Click “Apply”

Repeat the steps for finding explicit and implicit keywords with as many seed keywords as you have. This way, you capture a wide range of important keywords.
Step 4: Prioritize Based on Keyword Metrics
Next, you’ll gather intel about your keywords. This will help you prioritize the inclusion of the most lucrative ones.
A tool like Keyword Manager from Semrush can help.
You already have your spreadsheet with your list of terms, so select the option to “create a regular list” at the bottom of the page.

Give your keyword list a name and click “Create list.”

Click the “Add keywords” button in the upper right.

Add up to 2,000 keywords from your spreadsheet. When you’re done, click the “Add keywords” button.

On the default “Table” tab, you’ll see important metrics for your keywords.

These include:
- Search intent: Describes the intent of the searcher. You can tell whether the search was informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial.
- Search volume: Tells you how many times people search for that specific keyword each month.
- Trend: Describes how the search volume for the keyword has changed. You can tell whether its popularity is increasing or decreasing.
- Click potential: Displays how likely people are to click through the website to learn more about their query.
- Keyword difficulty: Measured in percentage, this metric shows you how difficult or easy it is to rank for the keyword. 1% KD means it’s easiest to rank for the keyword, while 100% means it’s the hardest.
Using this information, you can prioritize your list of relevant keywords based on your goals.
For instance, since your ads are designed to drive action, you probably want to prioritize search terms with transactional or especially commercial intent. You want to include words in your content that have a healthy search volume, but aren’t too difficult to rank for. A higher click potential is good.
When you incorporate those keywords into your content, your page has a better chance of being visible in the results. And being clicked on by the right type of audience.
From here, you can add the metrics from step one to your spreadsheet and sort the table based on your priorities.
How to Structure Local Keywords
Imagine customers searching for your business online. To find you easily, they’ll likely use keywords related to what you offer (“bakery”) and include their location (“Miami”).
So, you’ll want to structure local keywords effectively. It’s about combining relevant search terms for your business with the specific city, town, or area you serve.
Let’s say you own a bakery in Miami. Here’s how you can structure your keywords:
- Main target keyword + location: This is the most basic and common structure for local keywords. Simply combine your main service or product with the city or town your target customers are in.For example, “bakery in Miami.” This keyword clearly tells searchers what you offer (pastries) and where you’re located (Miami).
- Include specific service or product you sell: Refine your targeting by adding details about the services or products you offer.For example, “best custom birthday cake in Miami.” This keyword targets users searching for a specific type of cake (custom birthday cakes) within a particular location (Miami).
- Consider question-based keywords: These keywords recognize the informational intent behind question-based searches and can use that insight to attract potential customers.For example, “What bakery in Miami delivers croissants?”
Combine multiple strategies to create even more specific, long-tail keywords. For example:
- “Gluten-free bakery near South Beach Miami” combines dietary preference and precise location.
- “Can I order a cake online for same-day pickup in Miami?” targets convenience and location.
- “Best bakery for wedding cakes in Miami with affordable prices” combines intent, location, and price point.
Once you’ve identified and structured your main target keywords, it’s time to start optimizing your website and Google Business Profile to get your business to appear on local SERPs.
The Role of Competitor Analysis in Local SEO
Competitor analysis helps you understand who you’re competing with for space online. It reveals what terms people in your area are searching for. And how your competitors target those searches.
Competitor analysis also shows you untapped opportunities. By referencing your keyword list, you might discover the keywords that your competitors aren’t targeting. This creates a chance for you to leverage the opportunity and potentially rank higher for those keywords since there isn’t as much competition.
You can also benchmark your rankings for certain keywords against your competitors. This can help you set realistic goals and track your progress toward achieving them.
How to Do Competitor Analysis
Start by using Google to search for a local keyword phrase relevant to your business. Find your competitors who rank in the top three results on the SERP.
If you’re physically not in the location where your business operates, use a tool like I Search From. You’ll see the search engine results for the location you select.
Say you own a bakery in Miami. Open the tool, and select the United States as your Country and English as your language. The search term you’re exploring first is “Bakery.” And you want to see the results as if you are searching from Miami, Florida, so set that as your city.
It looks like this:

According to the search results, Rosetta Bakery and Arahi’s Bakery are among your main competitors.

Now that you know who it is, use Semrush’s Domain Overview tool to take a look at your competitor’s keyword strategy.
Simply enter your competitor’s URL, select your location from the drop-down, and click “Search.”

You’ll see important metrics like the domain’s organic search traffic and the top organic keywords it ranks for.

These metrics help you identify keywords you can target and benchmark your SEO efforts against your competitors.
Local Search Volumes and Keyword Relevance
Keyword research tools are valuable assets in SEO. They help you get a general sense of the keywords that are relevant to your business.
Tools like Semrush provide accurate metrics for larger-volume keywords.
However, keyword research tools can be less accurate when it comes to hyper-local search volume attributions and keywords with lower total volume, like less than 100.
Having said that, there’s nothing wrong with slight inaccuracies. These tools rely on estimates and are very useful for exploring relevant keywords for your business rather than precisely orienting your prioritization.
We suggest going for the keyword if you think it’s what your audience will search for, even if SEO tools show low search volume, such as zero or 30.
After all, you know your audience the best.
You can also use the Google Autocomplete feature to validate any keyword ideas you have.
To do so, enter your seed keyword idea (for example, “custom cake”) into Google’s search bar. Like this:

Google will automatically suggest related terms that people are using. If your idea comes up in an autocomplete suggestion, you can be sure that people are searching for it.
How to Map Keywords to Webpages
Keyword mapping is the strategic process of assigning target keywords—the words you want to rank highly for—to specific pages on your website. You map a keyword to a page by including it in your page URL, page title, and throughout the content on the page.
Keyword mapping is important for SEO. The prominence of a keyword on a page helps Google determine its relevance when would-be customers use that keyword in a search. If the algorithm sees that your page is relevant to your target keyword, it’s more likely to push your website to the top of the SERP.
If Google can’t find the keyword on your page, it’ll be harder to appear at the top of the SERP.
It’s important to be intentional about how you map keywords. If you target the same keyword on multiple pages serving similar purposes, for instance, Google will see them as duplicate pages and struggle to identify the best result to rank.
To organize your mapping effort, here’s a free Keyword Mapping Template by Semrush you can use:

Use this template to organize your keywords and allocate the primary keywords to relevant pages on your website.
The goal is to satisfy search intent by matching each keyword with the relevant page, which has the most potential for ranking high in SERPs.
When you map keywords on your website, you’ll be:
- Optimizing pages for the most relevant keywords
- Structuring your content throughout the website
- Preventing keyword cannibalization
- Gaining higher visibility in relevant SERPs
How to Optimize Your Google Business Profile
Your website isn’t the only online property to optimize. Your Google Business Profile is a dynamic snapshot of your business that enables users to gather basic information about your offerings right from the SERP.
For example, customers can view images of your location, see your address, make an online reservation, read reviews, and contact you.
Here’s what it looks like:

To get your business profile to appear on the SERP, you need to optimize your Google Business Profile with relevant keywords your would-be customers are searching for.
Optimizing your Google Business Profile helps to get you:
- Better local rankings: Google’s algorithm looks at relevance and proximity for local searches. But it also considers the quality of information.Optimize your Business Profile by including your target keyword in your business description and updating your address to be as specific as possible. That way, Google has all the information it needs to rank it in relevant local search results.
- More customers: An optimized Business Profile lets users find your business in local keyword searches.They can then call you, read reviews about your business, visit your website, discover your products and services, make a reservation or book an appointment, request a quote, and more.
Here’s how to apply the local keyword insights from your research to your Google Business Profile:
- Business description: Include relevant keywords in your business description. Be careful not to force them in. Just like in any other SEO-optimized content, insert the keywords naturally into the text.
- Photo titles: Name your images before you upload them to your Google Business Profile. Use descriptive file names and include relevant keywords naturally.Take an image of your storefront as an example. Change the generic file name like “Image_123” to a more descriptive one like “bakery near South Beach Miami.”
- Categories: Make sure your Google Business Profile is categorized accurately. The categories should match your services and products. Try to choose category names that resemble or match your target keywords.
- Updates: Use this section of the Google Business Profile to post updates relevant to your business.For example, post an update when you’re hosting an event. Or when you’re adding a new product or service. Make sure to include relevant keywords in your updates. This will help signal the Google algorithm that your profile satisfies a certain search intent.
Like this:

Additionally, your rankings can benefit from the keywords people use when they review your business.
For example, when you search “croissants near South Beach Miami,” you’ll notice that the places that come up on top results have reviews highlighting their croissants.

While you can’t control the reviews customers leave for your business, you can encourage them by providing excellent service. You can also consider offering incentives that increase the quantity of reviews you receive. Like giving free coffee to satisfied customers who leave positive reviews.
Further reading: Google Business Profile: How to Set Up & Optimize Your Listing
Ready to Perform Local Keyword Research for Your Business?
Your local SEO success starts with strategic keyword research.
When you understand what specific terms your target audience uses to find businesses like yours, you can optimize your online presence to attract more customers.
Here’s what you can do today to put these learnings into action:
- Brainstorm seed keywords: Make a list of words that describe your business, the products or services you offer, and the locations you serve.
- Leverage keyword research tools: Explore a basic tool like Google Keyword Planner or a more advanced one like Semrush to expand your list of specific keywords.
- Prioritize low-difficulty keywords with high search volume: Collect keyword data and focus on keywords that are relevant to your business, get good traffic, and are fairly easy to rank for.
- Optimize your website and Google Business Profile: Include your target keywords throughout your website content, meta descriptions, images, and Google Business Profile.
If you’d like to learn more about local SEO, read our definitive local SEO guide. It shows you what it takes to rank in the top three positions on Google search and teaches you how to optimize your Google Business Profile.
The post Local Keyword Research: 4 Easy Steps to Attract More Customers appeared first on Backlinko.